Vitamin B12 is a vital nutrient that aids in the production of red blood cells and the synthesis of DNA. As we age, our ability to absorb this essential vitamin diminishes. Since our bodies can’t produce it naturally, it’s necessary to get it from dietary supplements or animal-based food sources.
Many people don’t realize the importance of vitamin B12, which can lead to a deficiency. Astonishingly, around 40% of people in North America have this deficiency, with those suffering from chronic fatigue syndrome or fibromyalgia being particularly vulnerable.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Feeling Constantly Tired

Fatigue is one of the key indicators of a vitamin B12 deficiency, although not the only one. When you feel persistently tired despite adequate sleep, it might be a signal of deficiency. Vitamin B12 is crucial for red blood cell formation and oxygen transport. However, experiencing fatigue alone doesn’t confirm the deficiency; it’s essential to look for other signs.
Weak Muscles

If your body isn’t getting enough vitamin B12, your muscles may start to weaken as they depend on oxygen provided by red blood cells. Ensuring an adequate intake of B12 is vital in keeping your muscles strong.
Issues with Your Eyesight
A severe lack of vitamin B12 can damage the optic nerve and impede retinal blood vessels, potentially causing double vision, blurry vision, or even vision loss. If you notice problems with your eyesight, consult with a healthcare professional rather than diagnosing yourself.
Pale or Yellowish Skin

A yellow tinge to your skin could indicate a vitamin B12 deficiency, signifying the breakdown of red blood cells and the release of bilirubin. If you see such symptoms, or if jaundice appears, it’s crucial to seek medical advice without delay.
Smooth, Red Tongue
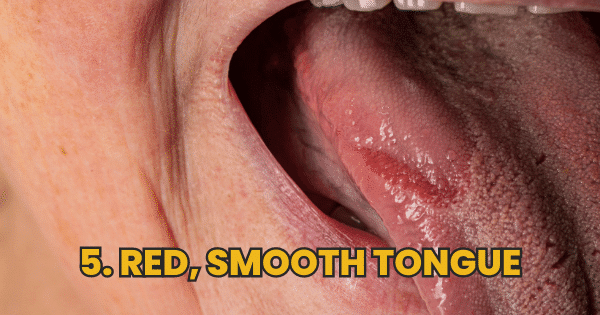
With a B12 deficiency, you might notice that the papillae on your tongue—which hold taste buds—begin to disappear, decreasing your taste sensitivity. This might cause pain towards the back of your tongue and impair your enjoyment of food.
Understanding What Causes the Deficiency

If the balance of bacteria in your gut is disrupted, it can obstruct the absorption of vital nutrients. Similarly, treatments such as chemotherapy can inflame the gut, affecting proper nutrient absorption.
Steps to Overcome the Deficiency
Revise Your Eating Habits

To tackle vitamin B12 deficiency, start by changing your diet. Introduce foods high in B12 like fish, chicken, lamb, beef liver, and chicken liver into your meals.
Consider B12 Supplements

If food sources aren’t a viable option, supplements like Methylcobalamin and Cyanocobalamin can be beneficial. Before starting any supplements, it’s important to consult with your doctor. These can be particularly helpful for those who don’t eat meat.
Include Quality Probiotics

Incorporating high-quality probiotics into your diet can aid in nutrient absorption. Excellent sources such as kefir, dark chocolate, and kombucha can support the effectiveness of vitamin B12.
Avoid Inflammatory Foods
Maintaining a healthy gut means cutting back on inflammatory foods, including processed foods, fast foods, fried foods, low-quality meats, and additives.
By maintaining a nutritious diet and taking supplements, you can ward off this deficiency and recognize early symptoms, ensuring prompt medical consultation when necessary.
Are you managing a vitamin B12 deficiency? How do you handle it? Feel free to share your experience!





