Washing Machines: Big Energy Users

Did you know that your washing machine is one of the biggest energy users in your home? It can really push up your electricity bill each year.
But don’t worry, there are ways to cut down on these costs. There’s a handy “secret” that many might not know about, which can lead to big savings. It’s as simple as pressing the temperature control button on your machine. This little button could be anywhere, depending on your machine model, but it’s usually easy to find.
A lady named Ms. Beth from the UK recently took to social media to share her tip for saving energy with washing machines. As a mother of two, she knows the importance of cutting costs. She noted that many washing machines automatically use 40 degrees of hot water, which uses much more energy than cold water washes. Many people forget to change it before starting a load.
Why Lower the Temperature to 20 Degrees?
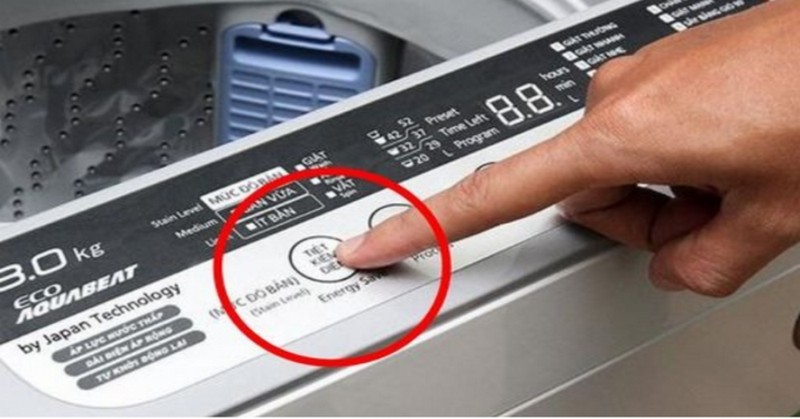

Ms. Beth suggests lowering the temperature setting to just 20 degrees. This simple change can reduce the running costs by up to 62%.
This is because heating water takes a lot of energy, and reducing the temperature reduces how much energy is needed. Don’t worry about your clothes not getting clean—modern detergents are designed to work well even in cold water, ensuring grime and bacteria are still whisked away.
Experts who specialize in cleaning clothing recommend similar advice. They often suggest washing clothes at 20 degrees to conserve energy. One expert said, “Your standard wash cycle can be quite costly in terms of energy usage. Opting for cold water wash instead will mean significant savings. Switching from a 40°C to a 20°C can save you 62%.”
Imagine the savings on your electricity bill just by making this adjustment. It’s not just about cutting costs; it’s also an easy way to be more environmentally friendly, using less energy for everyday tasks.
So next time you’re doing laundry, take a moment to check that temperature setting. Every little bit helps, and you might be surprised at how quickly those savings add up over time.